What Does High Platelets Count mean After Removal of your Spleen (Understand Thrombocytosis post Splenectomy)?
In order to understand the reasons of high blood platelets count after removing your spleen you must know some scientific basics for well understanding the meaning of elevation.
Spleen is that organ that located in the abdomen back to the rib cage on the upper left side, it’s one member of the human immune system to fight bacteria and other invasions as well as removing aged cells from circulation.
Removal of spleen is medically called “splenectomy”. Spleen removal comes after abnormally prolonged enlargement of spleen which lead to the untreatable chronic ITP disease (Acute low platelets count), ITP stands for Immune or Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura, when ITP blood test results reveal low platelets count but the reasons is unknown or may be the immunity system isn’t properly functioning, therefore, the spleen must be removed from the body to prevent serious complication.
How Does spleen affect platelets?
About third of platelets amount is circulating in the blood then stored in the spleen. The other 70% are circulating in the bloodstream for 7 – 10 days then become aged and the spleen capture them for recycling because the body’s immune system doesn’t use these platelets for blood clot formation during the period of 10 days. That was the best answer for the role of spleen in the life cycle of platelets and how do platelets leave the body?.
If you were asking, What’s the relationship between platelets and spleen? here’s the another answer
You must understand that in the steady state, the platelets and white blood cells are temporarily stored in the spleen in preparation for any possible confrontation with microbial invasions on the body, also the spleen filters the blood from the weak aged blood cells by engulfing and dissociate them into their raw components that will be used later for making new healthy cells.
If the spleen being sick, it will traps more platelets inside while the blood stream lacks of platelets, that is the reason the spleen become larger (i.e. accumulation of too many blood cells that can’t escape), and that’s why the blood platelets test reveal low platelets count “thrombocytopenia” when the spleen is larger than normal even though their are no symptoms may appear on the patient.
On the other hand, if the spleen is completely removed from the body through the surgical splenectomy operation, the platelets level abnormally increase in the blood stream because the spleen was the organ that responsible of controlling them, that’s why the blood platelets count appear elevated “thrombocytosis” after the surgery.
Does removal of spleen affect platelets count?
Yes, it can raise the platelets count in the blood test results because there’s no full management of the count by the body systems.
It’s a usual medical condition called Reactive or Secondary Thrombocytosis which means thrombocytosis (high platelets count in the CBC test) that caused by reactive disease or ongoing condition (e.g. removed spleen) that’s not related to the platelets themselves.
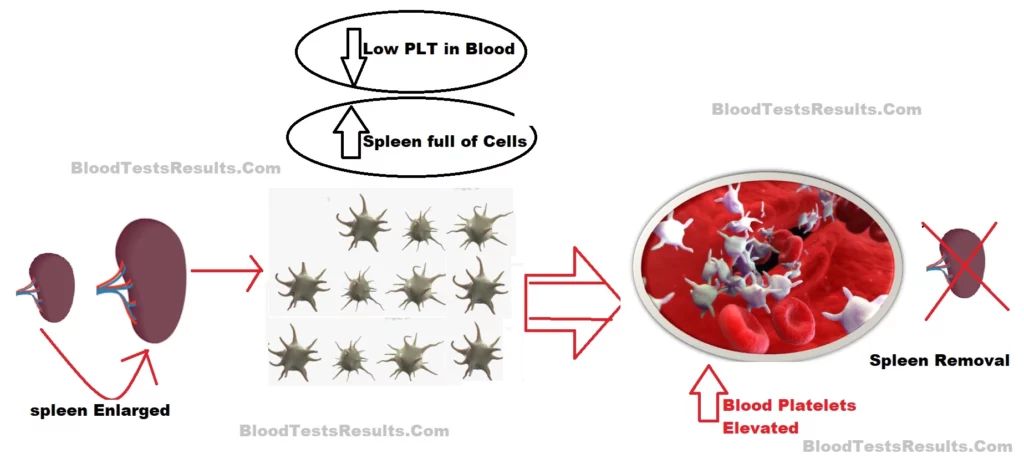
Is it normal to have elevated platelets count after splenectomy?
No, spleen removal is not a normal condition because the spleen helps the body regulates how many platelets should be in the blood?, thus, cutting the spleen from the platelets way will eventually cause abnormally high count in the CBC test.
Is high platelets count after spleen removal a good or a bad thing?
Elevated platelets after throw away the spleen from the body definitely is a bad thing but not too harmful, it’s called the “reactive thrombocytosis” which means increased platelets count in the blood due to reactivity of the blood system because the platelets count goes up after any injury to seal the wounds and contribute in the healing process, that’s why it’s natural and of good things to see high platelets in the blood after surgery, and it is a predictable lab finding after removing your spleen, so please feel reassured and don’t worry. However, too much platelets after splenic removal doesn’t found to cause the symptoms of thrombocytosis to appear because other organs such as the liver (liver Kupffer cells) may perform some of the spleen tasks which preventing the body from disruption or stop working. understand liver enzymes
When to worry about high platelets in the blood after splenectomy?
Splenectomy is a procedure of comparable risk, in other words, splenic removal surgery has 1.6% mortality rate “very small risk” and high success rate around 60%. which is satisfactory.
Because it’s of the blood homeostasis to see increasing in the platelets post-operative processes, even though, but the continuous rise in the number of platelets for a long period of time after the spleen removal becomes abnormal and undesirable, and other reasons may expected, thus you must be examined well by a specialist doctor.
High platelets count is one of the side effects if you have asplenia (your spleen is removed), other risks may include:
- Blood loss during the surgery, but it can be encounterable.
- Allergic reactions or breathing difficulties from anesthesia.
- The possible formation of blood clots, especially if the blood components and elevated platelets are out of control.
- Infection, because the spleen involving in the fight of infections.
- Stroke or heart attack if the thrombosis occur.
Although, it’s better to follow-up carefully after removing your spleen to ensure there’s no undesirable complications may occur.
Pregnancy with splenectomy is very risky and may lead to early delivery, also the elevated blood platelets as a consequence of splenectomy may lead to pregnancy failure. learn How to read pregnancy test?
Why high platelets are found in blood count if the spleen is removed?
If you were asking about the reasons and causes that lead to a high platelet count post splenectomy, here’s the correct answer.
Spleen store some platelets in the standby mode until such time as it is released when a bacterial infection occurs, thus the spleen is the primary organ that regulate the numbers of platelets by engulfing them, therefore, if the spleen is removed, the number of platelets will not be under full control and thus appear in tests more than the normal level specified for healthy people whose spleen has not been removed.
The spleen controls the number of platelets in the blood through releasing “splenic macrophages” according to the instruction come from the brain, a person who does not have a spleen has a low or no number of macrophages that control the number of platelets in the bloodstream, and thus show an increase in platelets than usual in laboratory results. Typically that was the answer for how does the spleen keep platelets count regulated not elevated nor reduced.
What’s the elevated platelets level with splenic removal?
After splenectomy Platelet counts may increase one third the count before the removal and may double elevated, e.g. if the platelets are 300,000 before the operation, it can go higher to 400,000 or 600,000 post-splenectomy operation.
How long will high platelets last post splenectomy operation?
The elevated platelet level may last about 1-3 weeks postoperatively, then the platelets count must re-stabilize and appear within normal limits after the surgical wounds healed and any delay of platelets elevation can be of another issue and must get follow-up. Surgical Wounds may heal in weeks, months, or rarely years it all depends on the whole status of the body after the spleen surgery then platelets count back to normal and don’t stay elevated forever.
What happens to blood test results after splenectomy?
Besides the high risk of blood clot formation, lab results other than high platelet counts post-splenectomy may look like this:
- Leukocytosis “high WBC” is the commonest finding in addition to elevated platelets after the spleen is removed.
- Monocytosis (high count of monocytes and/or Neutrophilia (high count of neutrophils cells in the blood count).
- Anemia “low hemoglobin” with low or normal red blood cells.
- MPV and PDW% may be elevated because the new platelets after splenectomy may be larger.
- Iron test and ferritin: may appear elevated or normal.
- Bilirubin test: may be elevated or normal.
- Sed rate test: may be elevated due to inflammation before and after spleen surgery.
High platelets and no spleen, what does that mean? Can no spleen cause high platelets?
It’s known that the disorders of the type “myeloproliferative” are responsible for pumping plenty of platelets “Thrombocytosis” into the bloodstream due to bone marrow’ issue, also if there’s no spleen (Asplenia) in the body “whether it is surgically removed or not-functioning”, the platelets population surely increase in most of people.
Conclusion:
The spleen is main player in immunity system and the terminator of blood cells including the platelets, thus if the spleen function interrupted or the spleen itself is removed, the platelets and white blood cells appear decreased during the splenomegaly (over-sized spleen), but after the spleen removal (splenectomy) the platelets and WBC released in too much quantities for up to a month then stabilize and back to the normal ranges because the liver cells replacing the spleen function and maintain the platelets count.
List the Diseases associated with impaired spleen function (Functional Asplenia) that can affect platelets count
- Sickle cell anemia elevate platelets level, in which the spleen enlarged and cause the platelets and red blood cells to accumulate and distort in their morphology, therefore the counts of platelets and other blood cells increase in the final lab results.
- Malaria, is another parasite infection of the blood that affect spleen and platelets count.
- Pneumonia
- Meningitis
If the platelets are found “high” on the automounting machines, the laboratory usually print the letter “A” or “H” near of platelets number in order to highlight it as abnormally high, learn the meaning of lab flag “H” near PLT
Understand the red flags on lab results
What blood test can detect spleen problems?
Spleen function test is the “complete blood count” or “CBC test” which include the full count of blood cells, during splenomegaly (large-size spleen) the blood suffers from pancytopenia which means “general count reduction of all types of blood cells “.
Hope you understand your platelets results after your surgery of spleen and it’s allowed to send questions about your lab tests and we promise satisfactory level of response.