What is this post talking about? to answer many questions like:
Do blood platelets elevate in patients with sickle cell disease?
How many platelets in patient of SCD? or To which level the platelets increase of a sickle cell disease person?
When to worry about high platelets if you're a SCD person?
Why do PLTs of the SCD patient elevate? is this bad or good?
Answers:
In a patient suffering of Sickle cell disease these results are often arise in the blood test results.
- Low hemoglobin "e.g. Hgb 4-7"
- Low Red blood cells and hematocrit "e.g. RBCs count# 2.0-3.5", "HCT, PCV% 10-20".
- High platelets count and become low after platelets count after a few period of time.
- Reticulocyte count may be elevated "2.5-15.0%of RBCs".
- Bilirubin test level may be elevated "Jaundice" if the hymolysis of blood occur "e.g. blood bilirubin 2 to 30".
- Iron levels in the blood may be depleted "e.g. free iron less than 5 and ferritin test less than 10 "
- Hemoglobin type-S is present in Hemoglobin Electrophoresis test "e.g. Hgb S >zero".
Explanation of Sickle cell in a glance
Sickle cell disease defined as a chronic inflammatory condition that increases the acute phase reactants blood levels and of course activation of more platelets which means abnormally high demand of platelets, thus how the platelets count high in the blood test of patients with sickle cells disease.
What happens in your blood if you have sickle cell disease?
The fluid that fills red blood cells and carries within it oxygen and nutrients is the "Hemoglobin", If you have a genetically defect in the manufacturing process of hemoglobin, the red cells become sickle-shaped and not like a disk as the normal, and therefore, the red blood cells that contain this distorted hemoglobin are unable to serve your body well in providing its needs from Oxygen and the necessary nutrients, accordingly, the body suffers from pain crisis, wasting and severe weakness, whether over a long period time or suddenly.
The lack of oxygen and food as a result of the rapid death of distorted red blood cells makes their number decrease, thus leaving your body exposed to all kinds of severe pain, swelling, poor vision, and weak or stunted growth.
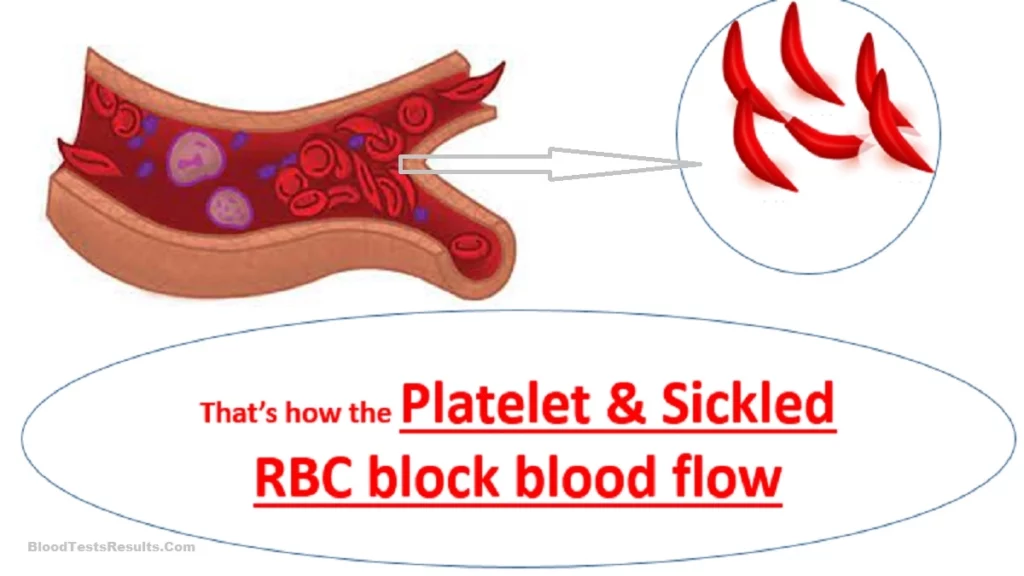
The complications of sickle cell erythrocyte malformation include:
When unhealthy red blood cells are distorted, it slows down the blood flow, and if the blood slows down, it can stop anywhere in the body and the cells clump over each others, thus a clot occurs in any organ, followed by ischemic necrosis or atrophy of the organ that the blood stops from enriching it. Actually that is the cause of all accompanying diseases to the sickle cell disease, e.g. acute chest disease, strokes as a result of slowing the flow of blood to the brain thus the blood may stop and clot may occur which may lead to cerebral edema and death occur.
The Blindness occurs as a result of poor blood circulation as well, Gallstones, and ulcers in the legs are among the complications that occur as a result of sickled RBCs.
What is the role of platelets in sickle cell disease?
Platelets are one of the types of blood components that gather and clump to form the clots "thrombosis" which occur as a result of the slow flowing of blood inside the blood vessels, and therefore the body thinks that the platelets are decreasing and consequently tries to produce more platelets and release them into the blood circulation more than the normal to compensate for the deficiency, and therefore a temporary increase in the number of platelets may occur in the test, but after a period of time, the bone marrow cannot produce more platelets which causes decline in platelets count to appear in the platelets blood test.
What does high platelets and low hemoglobin mean in sickle cell disease?
It is scientifically known that sickle cell disease mainly affects red blood cells and the reason is the manufacture of defective hemoglobin that cannot perform its function in transporting oxygen and nutrients, nor can it even support the red blood cells to become normal in shape, and then the red blood cells break faster than their normal rate of breaking Thus, the number of red blood cells in the blood count test decreases.
It is not common for other blood cells to be affected by sickle cell anemia, unless there are major complications such as peripheral or pulmonary clots, etc., then platelets are caught in the clots, and thus the number of platelets in the blood test decreases, low platelets is medically named Thrombocytopenia.
Also, when clots occur in peripheral parts of the body, atrophy or ischemia may occur to the next organ that follows the clot location, and thus the white blood cells move of all kinds to deal with the resulting inflammation, that's why you may show high WBC count in the white blood cell count test. And therefore, doing the full blood count (CBC&deff test) is better to follow-up sickle cell episode than the blood test for platelets count only, because the CBC test measures the count of all blood cells which helps the doctor make the right decision.
Are platelets increase or decrease in the sickle cells disease?
In fact, at the beginning of blood clots, the number of blood platelets may increase as a result of the increased demand for them at the site of clotting in the body, but when the clots grow and increase with time, the platelets are consumed in abundance, and therefore platelet deficiency appears in the blood count test.
Interestingly, many of the Medicines for sickle cell disease can also affect the levels of blood cells in the blood test.
If your child has sickle cell disease, testing for full blood cells count in the nearest laboratory can tell the doctors and staff about your child’s disease progression and how to effectively treat it.
Why does the SCD patient have low RBCs? Do you know why breath shortage is common in SCD patient?
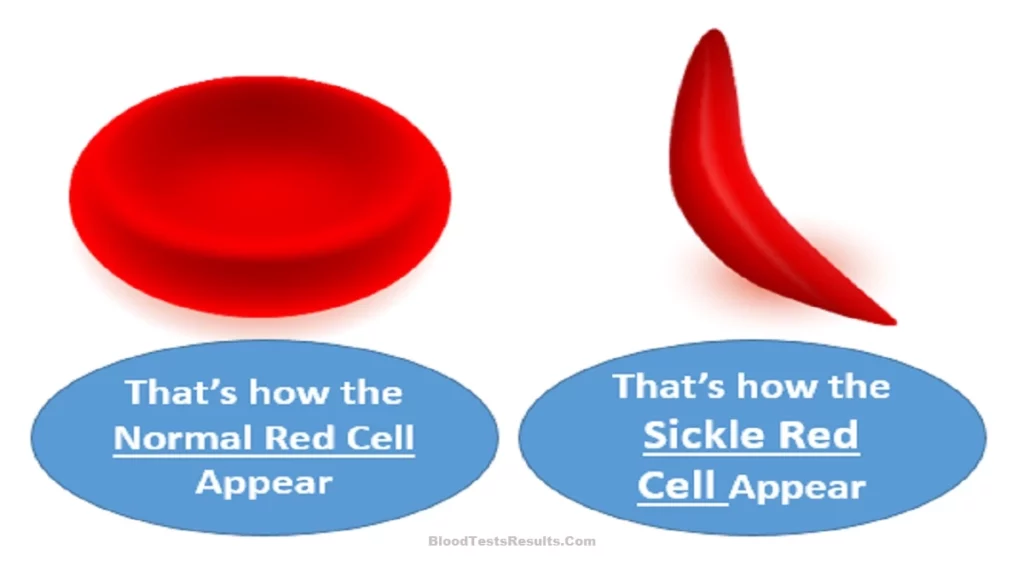
People with sickle cell disease have abnormal type of hemoglobin, called sickle hemoglobin or hemoglobin S, the red blood cells contain that defected hemoglobin which is unable to carry oxygen to other parts of the body leading to hypoxia or shortage of breath. Also SCD hemoglobin is the reason why red blood cells are damaging shortly and appear low RBC count in the blood test. That was the reasons of SCD patients have low hemoglobin or Anemia, and low RBCs count.
The Hemoglobin electrophoresis in sickle cell anemia is the best diagnostic test for "Hemoglobin S", the defected hemoglobin in the sickle-shaped RBCs, thus if the hemoglobin electrophoresis test is positive for "hemoglobin S" it means the person has the sickle cell anemia and must start treatment plan, but if the blood test results of "hemoglobin S" is negative or "zero" it means that the anemia isn't due to sickled red blood cells.
A blood smear examination is one of best tests to know if there're sickled RBCs or not, a blood smear is made in the laboratory from a small blood sample, then examined under the light microscope, if the RBCs appear like the sickle, the examiner write down how many sickle cells per red cells count and report it as a percentage
Do platelets elevate in all kinds of sickle cell crisis?
There are three main types of sickle cell crisis, vasoocclusive, aplastic, splenic sequestration, and hyperhemolytic. The vasoocclusive is the commonest sickle cell crisis type which may be occur suddenly (but lasts about 5 days) on a specific location of the body or can be occur in many organs.
Also, the causes of four main types of sickle cell anemia are different mutations in the below genes:
- Hemoglobin SS disease.
- Hemoglobin SC disease.
- Hemoglobin SB+ (beta) thalassemia.
- Hemoglobin SB 0 (Beta-zero) thalassemia.
- Hemoglobin SD, hemoglobin SE, and hemoglobin SO.
- Sickle cell trait.
Explanation of platelets count in the most common clinical manifestation of SCD, the vaso-occlusive crisis.
"Vaso" means in the vessels, occlusive means "obstruction", therefroe vasoocculative crisis means the blood clots that occur in the smallest blood vessels anywhere in the body because the circulation is being obstructed by the sickled RBC, the next organ will be painful ischemic (i.e. the organ that didn't get supply of blood because the flow is reduced or restricted), treatment of choice are the sufficient vigorous intravenous hydration fluids and analgesics and Normal saline and 5% dextrose in saline, to correct dehydration and to compensate continuing blood loss, both insensible and due to fever. Normal saline and 5% dextrose in saline may be used.
Do platelets high or low during acute chest syndrome?
Acute chest syndrome (ACS) is a deadly complication results of sickle cell disease in patients hospitalized with blood clots of the type "vaso-occlusive" crisis. Patients may have high platelet counts during steady state of the ACS, but platelets usually decrease during the acute vaso-occlusive crisis of the ACS. Doctors may aim on the platelets count to predict the development of ACS during admission in the hospital.
Low Platelets level during Vaso-occlusive crisis is a predictor of acute chest syndrome during sickle cell disease, because the increased active platelets increase the platelet-derived molecules for cellular adhesion which they're important markers of inflammation. Acute vaso-occulsive crisis will cause decline in platelets count in the blood test due to sudden blood loss, platelets increase at the beginning or during steady state as the demand of platelets increases at the first of the blood clots. Therefore, the patient with acute sickle cell crisis usually has low platelets count in the blood test results.
The aplastic crisis is a condition where the Red blood cell production is stopped leading to low platelets number not a high platelets number. Because the bone marrow is not producing red blood cells.
In the Splenic sequestration crisis, the sickled RBCs stay inside the spleen and can't go out which lead to enlargement of spleen "splenomegaly" and appear as large spleen, therefore the spleen traps more and more blood cells and platelets causing a big decline of platelets count in the CBC test. Because of that the blood platelets appear low not high during the Splenic sequestration crisis.
If a child has rapid drop in RBCs count "e.g. RBCs 3.0 while the normal is 5.0-7.0", the reticulocyte count test is high "e.g. Retics result is 8%, the normal 0.2-2.0", and hemoglobin Hgb 5.0, normal 11-14, severely low", they're clear indicators of hemolytic Anemia especially if the blood smear examination revealed that there're sickled cells RBCs, Hyperhymolytic crisis is another name for that complication of sickle cell anemia. Hyperhymolytic crisis due to infection, toxins, certain drugs, or blood transfusion will lead to acute loss of blood cells, that's why the RBC, WBC, Platelets appear low in the CBC test if the Hyperhymolytic crisis occurs.
When to worry about high platelets if you're a person has sickle cell disease?
If you or your child has sickle cell disease, his platelets count is probably normal in the steady state, then platelets count might increase "Thrombocytosis" at the beginning of the crisis, but platelets will decrease "Thrombocytopenia" later as the complications progress. therefore the count of platelets in the blood count test can be used as a good indicator of sickle cell disease complications which is of good news to know. Thus you may worry about platelets is they rapidly drop or elevated.
Thus, the platelets count in the different types of sickle cell disease is well explained, but if you have lab results that need to be cleared, we can do it for you, the service is still free yet.
