Progesterone levels chart from day 1 of your period to the early pregnancy and late pregnancy, progesterone level 2,5,10,18,400 explained with interpretation of target serum progesterone levels after using progesterone pills, suppositories, IM and fat injections.
If you’re confused about ovulation and pregnancy signs, normal progesterone levels chart, high progesterone levels, and low progesterone levels charts are exclusively decoded.
Test name at lab: serum progesterone, prog test, PGSN, Progesterone (P4)
Error writing: progstrone, progesteron, and progestrone
Looking for: What does progesterone do?
In general, normal serum progesterone test results fall in the following ranges: men, postmenopausal women, and women at the beginning of their menstrual cycle: 1 ng/mL or under. women in the middle of their menstrual cycle: 5 to 20 ng/mL. pregnant women in their first trimester: 11.2 to 90 ng/mL.
Also, there is a very strong connection with HCG levels and if having twins or single pregnancy.
Average progesterone levels chart
First two weeks of the period is 1 – 3 ng/ml, third week of the period (first ovulation week) is 2.5 – 13.5 ng/ml or 10 – 41 nmol/L, and the average progesterone levels decline after ovulation is 13 – 3 ng/ml or 40 – 10 nmol/L.
Note that: Some women have irregular periods which affect the day of ovulation and alter the expected normal levels for each woman.
Normal progesterone levels after ovulation day by day chart
Normal level is the optimal level seen in test results of healthy woman.
The first two week of your menstrual period progesterone ranges from 1 – 2 ng/ml.
Depends on if pregnancy occur or not, if pregnancy occur the corpus luteum produce more progesterone hormone to emphasize the uterus and grow the placenta to looking the baby after, 8 weeks (on average) after implantation the luteal-placental shift declare that the placenta is the responsible organ to produce much more progesterone and for growing the baby which results in multiplication of progesterone concentrations in the blood of pregnant woman.
Biological reference ranges:
- At the day 17 (3 days after ovulation): 3 – 9 ng/ml, or 12 – 30 nmol/L.
- At the day 21 (7 days after ovulation): 8 – 19 ng/ml, or 24 – 68 nmol/L.
- At the day 25 (3 days before period): 4– 15 ng/ml, or 10 – 45 nmol/L.
Variable normal reference ranges due to different women and cycles:
- At the day 17 (3 days after ovulation): 3 – 18 ng/ml, or 8 – 60 nmol/L.
- At the day 21 (7 days after ovulation): 2.5 – 23 ng/ml, or 5 – 73 nmol/L.
- At the day 25 (3 days before period): 1.5 – 20 ng/ml, or 3 – 62 nmol/L.
Middle luteal progesterone level is corresponding to day 21 in 28 days’ menstrual cycle (learn. how to calculate ovulation day?)
Progesterone level day 21 of your cycle is equal to non-pregnant female level, means that days 21 is an evidence of ovulation and doesn’t mean you’re pregnant or not.
Biologically the normal day 21 progesterone level is any value more than 5 ng/ml, the Average progesterone levels on middle ovulatory phase is 13 ng/ml or 40 nmol/L
Read more>> day 21 progesterone
Progesterone level chart if not pregnant
If you’re ovulated but no pregnancy occurs and no egg is fertilized, the serum progesterone level will begin to fall after corpus luteum lysis.
The expected progesterone levels before ovulation (days 1, 3, 5, 7, 10, 12, and 13) and if not pregnant is 2 – 5 ng/ml or 5 – 15 nmol/L.
Progesterone level chart if pregnant
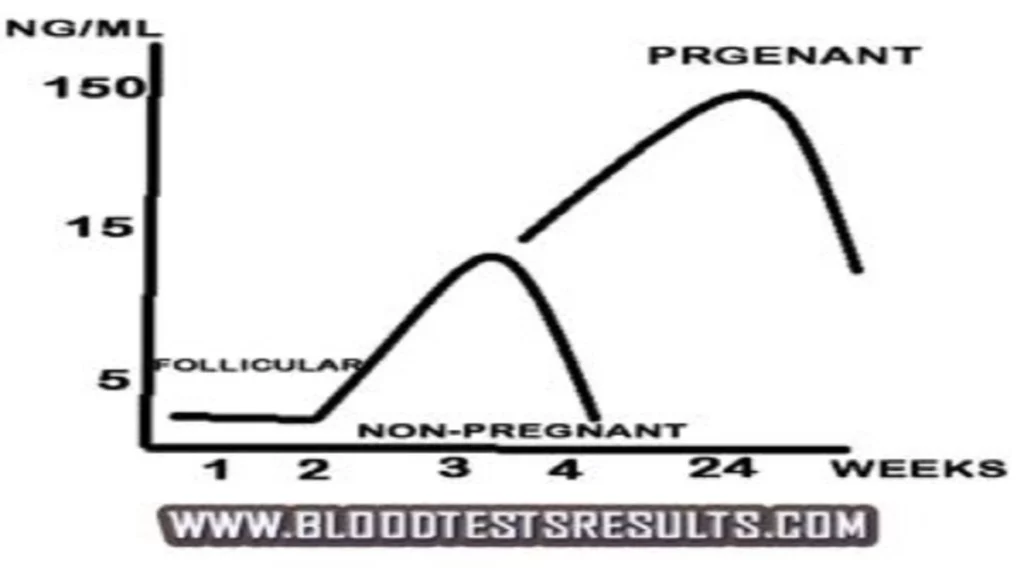
During human pregnancy, progesterone is produced in increasingly high amounts by the ovaries and placenta. At first, the source is the corpus luteum that has been "rescued" by the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) from the conceptus.
However, after the 8th week, production of progesterone shifts to the placenta. The placenta utilizes maternal cholesterol as the initial substrate, and most of the produced progesterone enters the maternal circulation, but some is picked up by the fetal circulation and used as substrate for fetal corticosteroids. At term the placenta produces about 250 mg progesterone per day.
An additional animal source of progesterone is milk products. After consumption of milk products, the level of bioavailable progesterone goes up.
Normal progesterone levels during pregnancy chart in nmol/L and ng/ml
Guideline to Progesterone levels during pregnancy recommend these chart levels:
- Progesterone levels in early pregnancy is 1-28 ng/ml (3.18 - 89 nmol/L) Mid Luteal Phase.
- Average progesterone levels is over 10 ng/ml (32 nmol/L) for un-medicated cycles and over 15 ng/ml (48 nmol/L) with medication use.
- First trimester progesterone levels are 9-47 ng/ml or 28.5 – 149 nmol/L.
- In the first trimester, levels of progesterone rise exponentially, and then they plateau.
- Second trimester progesterone levels are 17-146 ng/ml or 54 – 464 nmol/L.
- Third trimester progesterone levels are 55-200 ng/ml or 175 – 636 nmol/L
- In late pregnancy, the body produces progesterone hormone approximately 250 mg per day, 90% of which reaches maternal blood circulation
- After delivery or abortion progesterone level is decreased massively fast.
Progesterone levels chart after medication with progesterone Oral/IM/IV

Progesterone hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is used for menopause, hypogonadism, and transgender females.
Manufactured progestogens, or progestins, and derivatives include medroxyprogesterone acetate and norethisterone.
The half-life of progesterone in blood circulation is only approximately 5 minutes but differs for every pharmaceutical form.
- Oral micronized progesterone (OMP) target levels
Relatively short duration of action, so that it is often prescribed in divided doses of two or even three times daily.
Significantly elevated serum progesterone levels are maintained for about 12 hours and levels do not return to baseline until at least 24 hours.
- 100 mg dose of Vaginal and rectal progesterone target levels
In the form of a gel or suppository,used for birth control, results in peak levels at 4 hours and 8 hours after dosing, respectively, with the levels achieved being in the serum luteal phase range, gradual decline after 24 hours and serum progesterone levels typical of the follicular phase.
- Topical progesterone target levels
In the form of creams and gels (progesterone cream, Progestogel), exhibits very low progesterone levels in the blood circulation according to clinical studies (<3.5 ng/mL) of progesterone in blood circulation which is insufficient to confer endometrial protection from unopposed estrogen.
- Intramuscular progesterone injection target levels
Peak concentrations of progesterone are seen 2 – 3 hours after ingestion and the half-life is prolonged at 16 – 18 hours and high concentrations achieved.
Intramuscular injection of 10 mg progesterone in vegetable oil, maximum plasma concentrations are reached at approximately 8 hours after administration, and serum levels remain above baseline for about 24 hours.
How much progesterone in the blood test after progesterone shots? and what’s the target level reached by using the progesterone IM injections?
Average maximum serum concentrations after IM progesterone shots:
- Doses of 10 mg intramuscular progesterone injection increase the serum progesterone to 7 ng/mL
- 25 mg progesterone dose, raises progesterone level to 28 ng/mL, results in normal luteal phase serum levels of progesterone within 8 hours,
- 50 mg dose raise levels to 50 ng/mL
- A 100 mg progesterone dose produces mid-pregnancy levels.
At these doses, serum levels of progesterone remain elevated above baseline for at least 48 hours, with a half-life of about 22 hours.
- Subcutaneous progesterone injection levels
Prolutex once daily in Europe.
Less risk of injection site reactions, and less painful relative to intramuscular injection, the half-life of this progesterone injection under skin is 13 to 18 hours, which is similar to the half-lives of OMP and intramuscular progesterone
Taking progesterone under skin is rapidly absorbed and has been found to result in higher serum peak progesterone levels in compared to intramuscular oil injections.
Men and children normal progesterone levels chart:
Progesterone levels are relatively low in children. Healthy adult males have normal progesterone levels similar to those in women during the follicular phase (menses) of the menstrual cycle.
In males 16 years and elders 0.27 - 0.9 ng/mL or 0.86 - 2.9 nmol/L.
Normal kid’s progesterone (Female or male 1–9 years) levels 0.1 - 4.1 or 4.5 ng/mL or 0.3 – 13 nmol/L.
Read: what does Progesterone do in men and children?
Progesterone 0.0 nmol/L and undetectable
Very low progesterone levels are not usually seen but always there is a trace amount, However after delivery of the placenta and during lactation, progesterone levels are very low.
Normal progesterone levels in woman postmenopausal:
Progestrone mostly produced in females by the ovaries, the shutting down (whether by natural or chemical means), or removal, of the ovaries inevitably causes a considerable reduction in progesterone levels
Normal progesterone after menopause <0.2 – 1 ng/mL, or <0.6 – 3 nmol/L
Reference: look Clinical Chemistry Resources number (1) at: Resources page.
We're welcome free questions and explanations for your Progesterone blood test results.
