The short answer is, when HIV viral load is a high number and CD4 result is low, it means that the AIDS virus is working and still destroying your immunity power, as CD4 represents the immunity power and viral load represents the viremia, and below is the detailed information.
- What are HIV and AIDS?
- What is Viral Load
- What is CD4
- Normal HIV
- Normal CD4
- Classification of AIDS based on viral load
- Case Study example
What does CD4 stand for?
CD4 represents the receptor antigen found on some white blood cells (helper T-Cells), monocytes, and macrophages cells in the human blood, CD4 cells are prone to attack by HIV virus, that's why "the CDC" used to use CD4 count for determining the immunodeficiency status of the AIDS-infected persons, but not CD4 count alone, because the CD4 count can go down in many diseases other than HIV infections, such as a person on chemotherapy, Herpes virus, pneumonia, or even one have a flu.
"CD4+" is a blood test used for measuring the count and percentile percentage of white blood cells that carry CD4 antigens.
What do HIV and AIDS stand for?
"H" is for Human, "I" is for Immunodeficiency, "V" is for Virus, and therefore the HIV word is a medical short form for the sentence (human immunodeficiency virus), HIV is a virus that attacks the human immune system and can lead to the disease AIDS if not treated, AIDS is a medical short form for the disease (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome).
So that, not all HIV is AIDS but AIDS is necessarily HIV.
HIV 1,2,0 blood test; is a rapid quantitative test that can be done by two drops of the blood at home, two lines results mean positive (i.e. the antibodies to HIV-1, HIV-2, and Subtype O is found in the whole blood, one line (opposite to the letter "C") always means negative HIV Antibodies result, a negative result means you're not infected with HIV virus at all or you infected but your body hasn't produced antibodies to the virus yet which called (window period). Read more about HIV 1,2,0 test
If you're in the window period, you must retest for HIV after 4 weeks at least. If you need a more accurate HIV test is the nucleic acid test (NAT) which can detect HIV infection 10 to 33 days after HIV exposure. read the list of HIV tests
What does Viral Load stand for?
A viral load test or HIV PCR is the laboratory method of counting HIV virus such as real-time PCR technique so that when a blood test report says a viral load result is 100, it means the count of virus units in your blood is 100, and when viral load result is written "zero" or "below detection limit" or "Negative", it should mean that your blood has no sufficient viral units to be counted by the PCR instrument.
And Of course, the Viral load (VL) test result strongly predicts the progression to AIDS disease which leads to death and a surrogate marker for the response to ART therapy treatment.
Acute HIV infection is defined as the period after exposure to the virus but before seroconversion.
Seroconversion or the window period is the period during which the body starts producing detectable levels of HIV antibodies. This usually occurs several weeks after initially contracting the virus. During seroconversion, a person may experience flu-like symptoms, such as fever and body aches.
HIV Viral Load Chart (quantitative HIV PCR); HIV-1 RNA:
Below the HIV test chart that shows normal ranges of viral load for untreated patients who are not given medical treatment and those for under-treatment patients:
| Condition | Normal Range(copies/mL) | HIV Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Undetectable viral load, Untreated Person, or 1-3 months after treatment | Below 50 | Zero |
| Low-Level Viremia | >50-1,000 | 5-30% |
| Medium-Level Viremia | >1,000-10,000 | >30-50% |
| High-Level Viremia | >10,000-100,000 | >50-75% |
| Extreme-high-Level Viremia | >100,000 | >75-100% |
ART means anti-retrovirus therapy, a treatment method or regimen for patients with the HIV virus.
LLV stands for Low Level Viremia which refers to two or more consecutive HIV-1 RNA test results at least 50 copies/ml, a person in the LLV classification has an estimated prevalence of between 5 and 30%. Low-level-viremia range is between 50 and 1000 copies/ml during ART According to WHO guidelines. Patients in the LLV range can pass HIV virus to others.
Some guidelines categorize LLV range during Antiretroviral treatment into three subcategories to ease the follow-up process.
Undetectable viral load means that your blood and body fluids don’t have sufficient HIV virus RNA units to progress to AIDS disease or to pass HIV virus to another partner during sex, in other words, you are neither infected nor infectious. So that No, you cannot infect someone if your viral load is undetectable.
Medium and high level viremia means the HIV virus units is between 1,000 – 100,000 copies per mL of blood, which is sufficient to let the HIV virus pass into blood and most of body fluids such as mucus, urine, stool, and semen. Semen infection with HIV viral units let the virus transported during unprotected-sex with a partner and become infectious by a high degree.
Extreme level viremia is any HIV count greater than 100,000 viral copies per mL of blood, this range represents the highest risk to develop AIDS disease and the highest mortality. A person who carries more than 100,000 units of the AIDS virus in his blood must be quarantined as soon as possible because he is in a very contagious state to others and is at great risk of death.
For specialists only, FDA Approved Quantitative HIV-1 (Viral Load) Assays
The below table contains updates from the Association for Molecular Pathology which maintains an up-to-date listing of “FDA Cleared/Approved Molecular Diagnostic Tests.” To access this list, please visit http://amp.org/, under “Resources.”
Below, the table shows the lowest detection limit and the highest detection limits of viral load tests in different kits.
| MANUFACTURER | TEST Name | METHOD | LINEAR RANGE (copies/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Roche Molecular Diagnostics | Amplicor HIV-1 Monitor | RT-PCR | 400–750,000 standard 50–100,000 ultrasensitive |
| BioMerieux, Inc. | Nuclisens | NASBA | 176–3.47*10^6 |
| Siemens Health Care Diagnostics | VERSANT HIV-1 RNA 3.0 | bDNA3 | 75–500,000 |
| Abbott Molecular, Inc. | Abbott Real-Time HIV-1 | Real-time PCR | 40–10^10 |
CD4 Normal chart
Below are universal normal ranges, but each laboratory can make its range-chart.
The normal range for a CD4 count is between 400 and 1,600 cells per microliter of blood (uL), it means the AIDS-negative person when do CD4 count must see his result in between these limits.
Normal CD4% is >25%, it means normal person must have more than 25% of the counted cell contain CD4 antigen.
A case study from messages sent to the official Facebook page
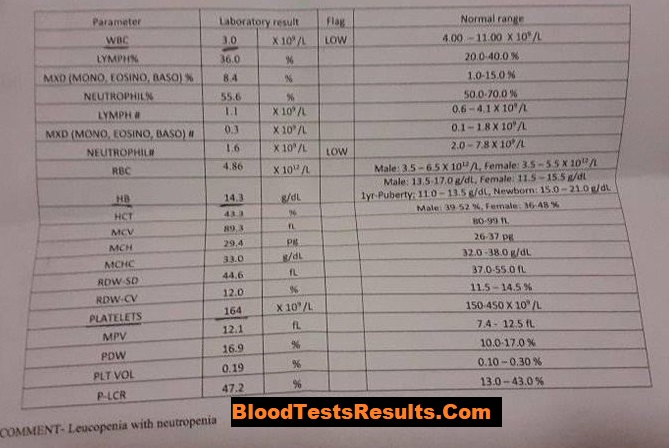
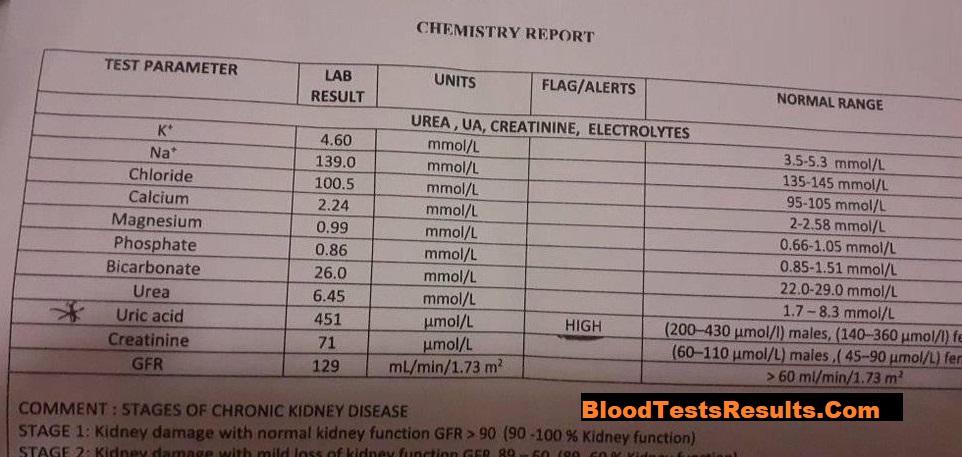
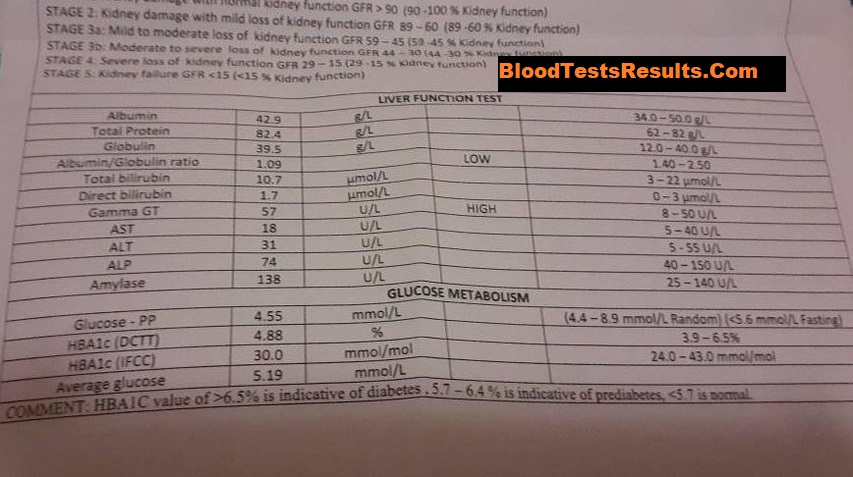
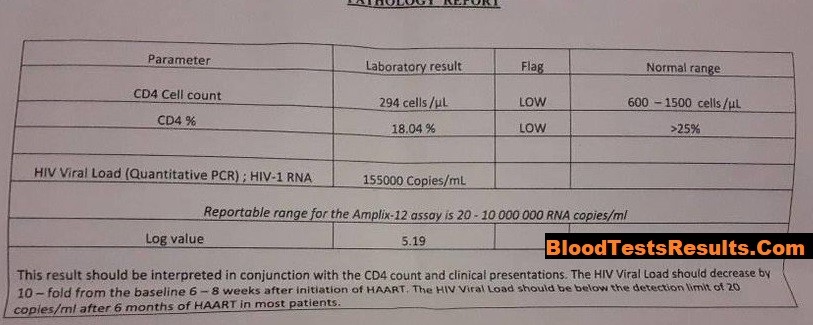
In that case, we can find low CD4 count and low CD4 percentile percentage with high-level-viremia more than 150,000 copies of HIV virus, these results present progressive HIV infection which need treatment and quarantine.
CBC test results of the patient show the low total count of white blood cells and low neutrophil cells which is an indicator of low CD4 T cells as well, the low the neutrophil cells the higher the HIV viral load.
Hope that information helps and let me know if you need more information.
